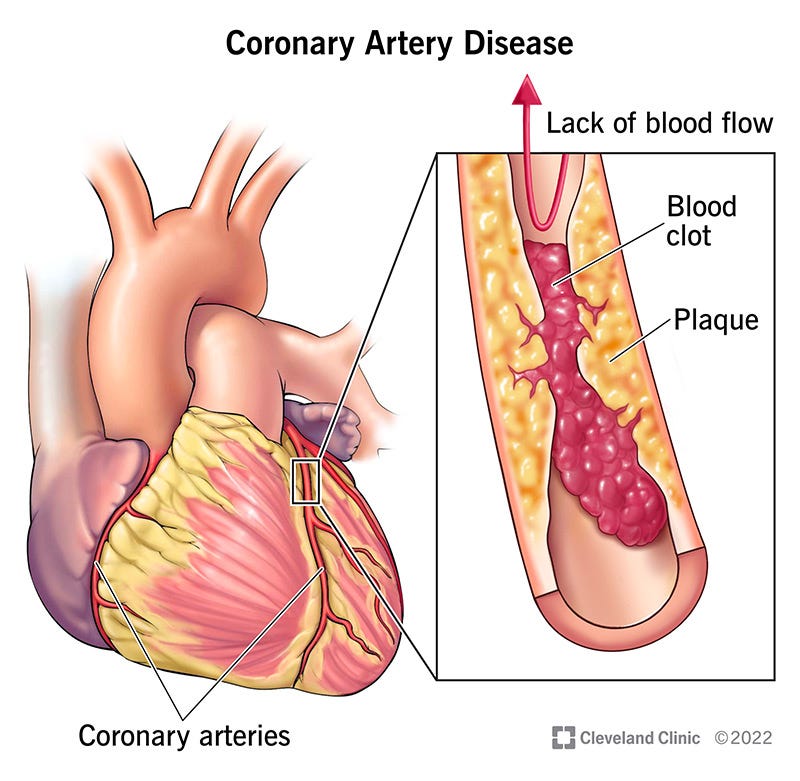
Coronary heart disease (CHD), alternatively referred to as coronary artery disease (CAD), is responsible for most deaths in America. CHD arises when coronary arteries, responsible for delivering blood rich in oxygen to the heart, become constricted and obstructed with a build-up of plaque. Over a period, atherosclerosis, a build-up of plaque, reduces blood flow, putting a victim at high risk for heart attack and other life-threatening complications. CHD progresses undetected for years but can have deadly consequences when not addressed.
A variety of factors contribute to developing CHD, most of them being a function of one’s life choices. Cigarette smoking, high blood cholesterol, high blood pressure, obesity, poor nutrition, and inactivity contribute immensely towards developing heart disease. Diabetics and a family with a history of CHD can also contribute towards increased vulnerability towards heart disease. Although factors such as one’s genetic make-up cannot be altered, life choices can go a long, long way in preventing and controlling disease development.
Symptoms of CHD depend on its severity level. Most sufferer’s have a heart attack and a sharp, burning sensation in the heart, a sign of not enough blood rich in oxygen getting to the heart, a state of angina. Shortness of breath, weakness, and a sharp, burning sensation in the arm, shoulder, jaw, and upper part of the back follow soon afterwards. In extreme cases, a full stop in blood circulation can cause a heart attack, and in most cases, a heart attack can manifest with a sharp, burning sensation in the heart, but in a few, no symptoms at all, a state of a "silent" heart attack.
Diagnosing CHD entails a variety of medical tests that evaluate heart function and detect any obstruction. Electrocardiograms (ECG), stress tests, cardiac catheterization, and nuclear scans most frequently evaluate heart function. Treatment varies with disease severity but can include changing one's lifestyle in terms of having a heart-smart diet, exercising regularly, not smoking, and controlling blood and cholesterol levels. Antiplatelets, drugs for lowering cholesterol, and blood pressure drugs can even be taken under medical supervision. In severe cases, medical interventions such as angioplasty, implantation of a stent, or coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) can be performed to rechannel blood to the heart effectively.
Coronary heart disease is a curable but life-threatening disease. By knowing its cause, early symptoms, and taking preventive actions towards a healthy heart, one can effectively avert complications. Consulting a doctor and changing one's lifestyle can go a long distance in averting and controlling life-threatening disease.
Sources:
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/coronary-heart-disease
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/coronary-artery-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20350613
Written by Aditi Avunuri from MEDILOQUY